|
Structure |
Sample Message |
Related Messages
Description
Establishing a FIX connection involves three distinct operations: creation of a telecommunications level link, authentication/acceptance of the initiator by the acceptor and message synchronization (initialization). The sequence of
connection follows:
- The session initiator establishes a telecommunication link with the session acceptor.
-
The initiator sends a Logon<A> message. The acceptor will authenticate the identity of the initiator by examining the Logon<A> message. The Logon<A> message will contain the data necessary to
support the previously agreed upon authentication method. If the initiator is successfully authenticated, the acceptor responds with a Logon<A> message. If authentication fails, the session acceptor should shut down the
connection after optionally sending a Logout<5> message to indicate the reason of failure. Sending a Logout<5> in this case is not required because doing so
would consume a sequence number for that session, which in some cases may be problematic. The session initiator may begin to send messages immediately following the Logon<A> message, however, the acceptor may not be ready
to receive them. The initiator must wait for the confirming Logon<A> message from the acceptor before declaring the session fully established.
After the initiator has been authenticated, the acceptor will respond immediately with a confirming Logon<A> message. Depending on the encryption method being used for that session, this Logon<A> message may
or may not contain the same session encryption key. The initiator side will use the Logon<A> message being returned from the acceptor as confirmation that a FIX session has been established.
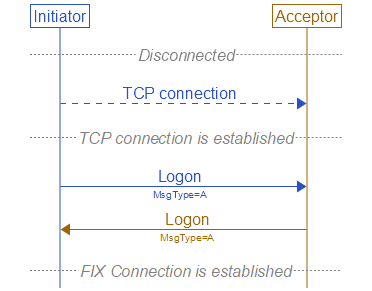 Successful Logon
If the session acceptor has chosen to change the session encryption key, the session initiator must send a third Logon<A> back to the other side in order to acknowledge the key change request. This also allows the
session acceptor to know when the session initiator has started to encrypt using the new session key. Both parties are responsible for infinite loop detection and prevention during this phase of the session.
- After authentication, the initiator and acceptor must synchronize their messages through interrogation of the MsgSeqNum(34) field before sending any queued or new messages. A comparison of
the MsgSeqNum(34) in the Logon<A> message to the internally monitored next expected sequence number will indicate any message gaps. Likewise, the initiator can detect gaps by comparing
the acknowledgment Logon<A> message’s MsgSeqNum(34) to the next expected value. The section on message recovery later in this document deals with message gap handling.
- It is recommended to wait a short period of time following the Logon<A> or to send a TestRequest<1> and wait for a response to it before sending queued or new messages in order to
allow both sides to handle resend request processing. Failure to do this could result in a ResendRequest<2> message being issued by one’s counterparty for each queued or new message sent. (see "Logon Message NextExpectedMsgSeqNum Processing" for an alternative approach)
- It is also recommended that an engine should store out of sequence messages in a temporary queue and process them in order when the gap is closed. This prevents generating resend requests for n->m, n->m+1, n->m+2, ... which can result
in many resent PossDupFlag(43)=Y messages.
- When using the ResetSeqNumFlag(141) to maintain 24-hour connectivity and establish a new set of sequence numbers, the process should be as follows. Both sides should agree on a reset time and the
party
that will be the initiator of the process. Note that the initiator of the ResetSeqNum<4> process may be different than the initiator of the Logon <A> process. One side will initiate the
process by sending a TestRequest<1> and wait for a Heartbeat<0> in response to ensure of no sequence number gaps. Once the Heartbeat<0> has been received, the initiator should send a Logon with ResetSeqNumFlag(141) set to Y and with MsgSeqNum of 1. The acceptor should respond with a
Logon
<A> with ResetSeqNumFlag(141) set to Y and with MsgSeqNum(34) of 1. At this point new messages from either side should continue with MsgSeqNum(34) of 2. It should be noted that once the initiator sends the Logon <A> with the ResetSeqNumFlag(141) set, the acceptor must obey this request and
the
message with the last sequence number transmitted “yesterday” may no longer be available. The connection should be shutdown and manual intervention taken if this process is initiated but not followed properly.
The Logon<A> message authenticates a user establishing a connection to a remote system. The Logon<A> message must be the first message sent by the application
requesting to initiate a FIX session.
The HeartBtInt(108) field is used to declare the timeout interval for generating heartbeats (same value used by both sides).
Upon receipt of a Logon<A> message the session acceptor will authenticate the party requesting connection and issue a Logon<A> message as acknowledgment that the
connection request has been accepted. The acknowledgment Logon<A> can also be used by the initiator to validate that the connection was established with the correct party.
The session acceptor must be prepared to immediately begin processing messages after receipt of the Logon<A>. The session initiator can choose to begin transmission of FIX messages before receipt of
the confirmation Logon<A>, however it is recommended that normal message delivery wait until after the return Logon<A> is received to accommodate encryption key
negotiation.
The confirmation Logon<A> can be used for encryption key negotiation. If a session key is deemed to be weak, a stronger session key can be suggested
by returning a Logon<A> message with a new key. This is only valid for encryption protocols that allow for key negotiation. (See the FIX Home Page
Application notes for more information on a method for encryption and key passing.)
The Logon<A> message can be used to specify the MaxMessageSize(383) supported (i.e. can be used to control fragmentation rules for very large messages which
support
fragmentation). It can also be used to specify the MsgTypes supported for both sending and receiving.
Structure
Sample Message
The '^' character is used to represent SOH character.
8=FIXT.1.1^9=116^35=A^49=BuySide^56=SellSide^34=1^52=20190605-11:51:27.848^1128=9^98=0^108=30^141=Y^553=Username^554=Password^1137=9^10=079^
Related Messages
|
 Successful Logon
Successful Logon